Arterial Ulcerations
Arterial ulcerations are a painful and potentially severe foot and ankle condition characterized by open sores or wounds that occur due to insufficient blood supply to the affected area. These ulcers primarily affect individuals with underlying arterial diseases, such as peripheral artery disease (PAD) or atherosclerosis, which lead to reduced blood flow to the extremities.
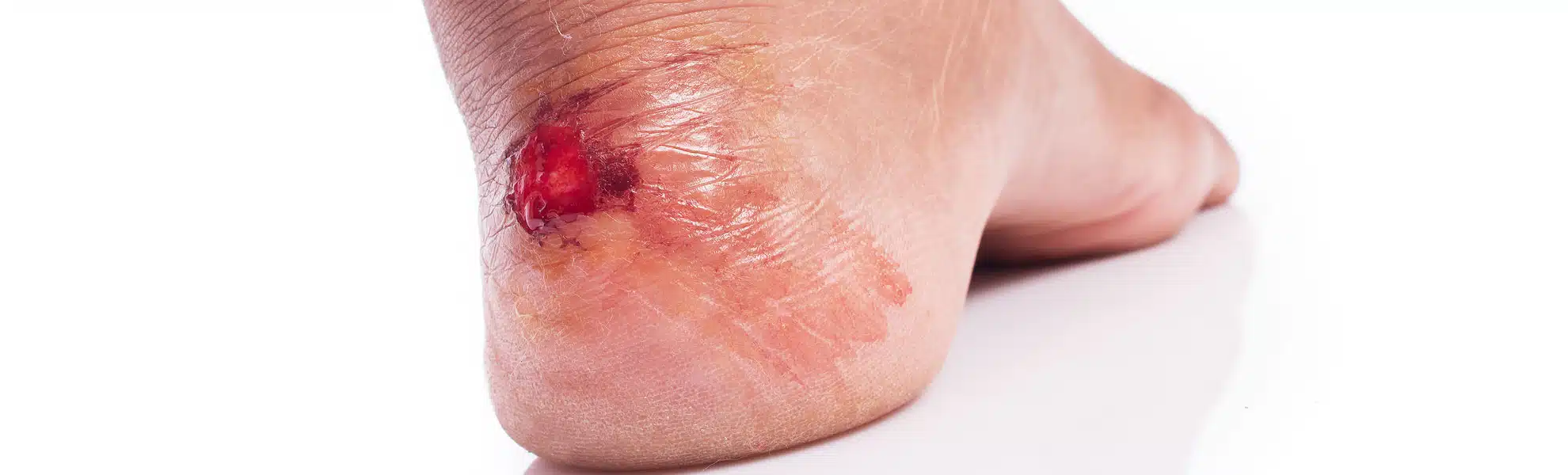
Arterial ulcerations in the foot and ankle typically develop when there is an inadequate supply of oxygen and nutrients to the tissues, causing them to break down and form open wounds. These ulcers are often located on the lower parts of the legs and feet, as these areas are farthest from the heart and, therefore, more susceptible to reduced blood flow.
Characteristics of arterial ulcerations include:
- Pain and Discomfort: Individuals with arterial ulcerations often experience severe pain, mainly when resting or at night. The pain is caused by tissue damage due to lack of oxygen.
- Wound Appearance: Arterial ulcers typically present as shallow, well-defined wounds with a pale or grayish appearance. The surrounding skin may be dry, thin, and cool to the touch.
- Delayed Healing: Arterial ulcers are known to be slow to heal and may persist for extended periods without proper intervention.
- Risk of Infection: These ulcers are more susceptible to bacterial contamination due to compromised blood flow and a reduced ability to fight off infection.
- Gangrene: In severe cases, untreated arterial ulcerations can lead to gangrene, a condition characterized by tissue death, which poses a risk of limb amputation if not addressed promptly.
- Effective management of arterial ulcerations involves a multi-pronged approach to improve blood circulation, facilitate wound healing, and reduce pain:
- Revascularization: In some cases, surgical interventions such as angioplasty, bypass grafting, or stent placement may be necessary to restore blood flow to the affected area.
- Wound Care: Meticulous wound cleaning, debridement (removing dead or damaged tissue), and specialized dressings are essential for promoting healing and preventing infection.
- Pain Management: Pain relief strategies, including medications and therapies, are employed to manage discomfort during healing.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, quitting smoking, controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and adhering to a nutritious diet can help improve overall vascular health.
- Compression Therapy: Compression stockings or bandages may improve blood flow in the affected limb.
Arterial ulcerations are a serious medical condition that requires prompt diagnosis and comprehensive treatment by healthcare professionals. Early intervention and a proactive approach to wound care are crucial for minimizing complications and preserving foot and ankle health.
Thermal injuries affecting the foot and ankle are a challenging and painful group of conditions resulting from exposure to extreme temperatures, whether heat or cold. These injuries encompass a range of severity, from minor burns and frostbite to more severe scalds and deep tissue damage. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and appropriate treatment for thermal injuries is crucial for the overall well-being of individuals with foot and ankle conditions.